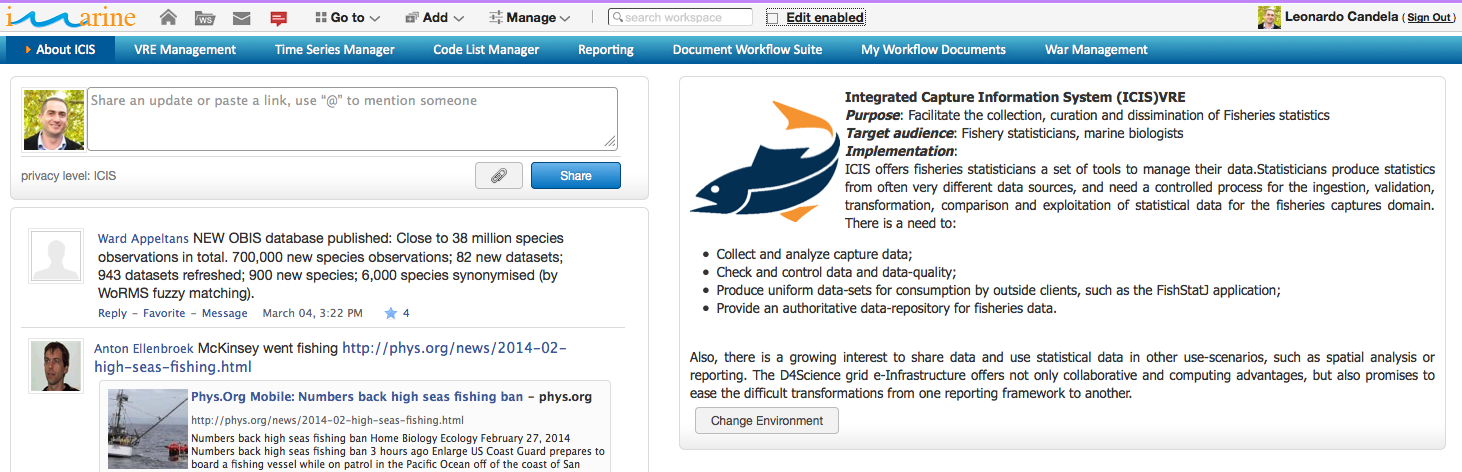
The ICIS Virtual Research Environment
Contents |
Description
The Integrated Capture Information System (ICIS) Virtual Research EnvironmentA ''system'' with the following distinguishing features: ''(i)'' it is a Web-based working environment; ''(ii)'' it is tailored to serve the needs of a Community of Practice; ''(iii)'' it is expected to provide a community of practice with the whole array of commodities needed to accomplish the community’s goal(s); ''(iv)'' it is open and flexible with respect to the overall service offering and lifetime; and ''(v)'' it promotes fine-grained controlled sharing of both intermediate and final research results by guaranteeing ownership, provenance, and attribution. offers fisheries statisticians a set of tools to manage their data. Statisticians produce statistics from often very different data sources, and need a controlled process for the ingestion, validation, transformation, comparison and exploitation of statistical data for the fisheries captures domain;
URI: https://portal.i-marine.d4science.org/group/icis
Functionality
The main facilities this VREVirtual Research Environment. offers are:
- Time Series Management: to enable users to import, curate and manage time series. This is a comprehensive and feature-rich environment that support data managers during the whole life cycle of data management from capture to publishing and visualisation. In enable data managers to import and transform CSV files in time series, i.e. tabular data having proper types associated with columns eventually referring to code lists – reference datasets representing recognized value instances of the elements the dataset is about, e.g., species, zones, countries. The environment guarantees that the time series are compliant with the defined types and code lists. Besides the curation, the environment supports the analysis of the data by enabling a user to (i) perform operations like grouping and filtering, (ii) producing charts and GIS maps (if the data have geographic features) and (iii) analysing the data via an R environment. Finally, the environment supports the publishing of time series in the infrastructure by equipping them with rich metadata so that such resources can be used in other application contexts;
- Code Lists Management: to enable the users to import and manage code lists, i.e. reference datasets representing recognised value instances of the elements the dataset is about. Such environment enable users to import CSV files or existing code lists from SDMX repositories, curate them when needed, inspect the current values, and produce and publish new versions that can be used during the curation phase of a time series. Code lists are annotated with rich metadata capturing attribution and lineage;
- Reporting facilities: to enable users to collaboratively produce reports consisting in complex documents characterised by well defined structures (templates). Via this facility, users can define new templates as well as collaboratively create new reports compliant with defined templates. Reports might contain diverse elements ranging from texts to images and tables, and such constituents can result from objects stored in the user workspace. Reports can be materialised in multiple formats including PDF, HTML and OpenXML;
- Documents Workflow facilities: to enable users (i) to define complex workflows (including steps and roles users should have to perform certain steps) governing the production of gCube documents, (ii) to instantiate such workflows to actual documents to be collaboratively created, and (iii) to monitor workflow execution;
- WAR Management: to enable authorised users to upload, deploy and monitor web-based applications packaged and distributed via the Web application ARchive (WAR) format. The upload phase enable a user willing to upload its web application to provide the system with the metadata needed for its management. The deployment and monitoring phase enable a user to select a machine (among the available ones), to deploy on it a web-application and to monitor its operational status;
- Workspace: to enable every user to store and organise the information objects he/she is interested to work with. In addition to that, the user is allowed to collaborate with other users by sharing objects and messages;
- VREVirtual Research Environment. Management: to enable authorised users (i.e. VREVirtual Research Environment. Managers) to manage other users using or willing to access the VREVirtual Research Environment.. VREVirtual Research Environment. Managers are enabled to (i) authorise users in accessing the VREVirtual Research Environment., (ii) assign or withdraw roles to users, (iii) remove users, and (iv) send a communication to the current users.
Data
The main datasets that are available via the services hosted by this VREVirtual Research Environment. include a series of code lists including FAO and IRD SDMX repositories.
Software
- (DONE) gCube 2.7.2 (December '11);
- (DONE) gCube 2.7.3 (February '12);
- (DONE) gCube 2.8.0 (March '12);
- (DONE) gCube 2.8.1 (April '12);
- (DONE) gCube 2.9.0 (June '12);
- (DONE) gCube 2.9.1 (August '12);
- (DONE) gCube 2.11.0 (October '12);
- (DONE) gCube 2.12.0 (February '13);
- (DONE) gCube 2.13.0 (March '13);
- (DONE) gCube 2.14.0 (May '13);
- (DONE) gCube 2.15.0 (June '13);
- (DONE) gCube 2.16.0 (July '13);
- (DONE) gCube 2.17.0 (December '13);
- (DONE) gCube 2.17.1 (December '13);
- (DONE) gCube 3.0.0 (March '14);