IOTC Area Predictive analysis
Description
The Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) is an intergovernmental organization that coordinates the regulation and management of tuna in the Indian Ocean. The commission publishes data about fishing activity, to be used by fishery managers for monitoring catch effort and ocean exploitation.
The experiment described in this page, focuses on the purse seine fishing activity.
This page reports an analysis to detect, monitor and predict such activity.
Hypothesis and Thesis
Premise
- The analysis benchmark is made up of a report about purse seine fishing activity in the Indian Ocean involving Yellowfin tuna.
Hypothesis
- The exploitation trends and the locations involved in fishing activity could be periodic and could be forseen.
Theses
- Basic statistical analysis, trends displaying and signal processing can detect periodic properties;
- Forecasting techniques can predict future exploitation.
Outcome
Starting from IOTC reports about purse seine fishing activity, in the Indian Ocean from 1997 to 2012, we detected the following phenomena:
1 an overall periodic, yet decreasing, number of Purse Seine fishing hours in the Indian Ocean; 2 a periodic trend in the visitation of fishing locations by vessels, with periodicity around 51 months; 3 an overall periodic variation of 12 months in the latitudes of the purse seine activity; 4 forecasted locations for the fishing areas in the following years; 5 a list of the most exploited areas at 10 degrees resolution; 6 an overall periodic reduction of the Catch per Unit Effort (CPUE) is showed in one highly exploited 10-degrees area.
Analysis
The bechmark for our analysis can be found here. The dataset was extracted from the reports by IOTC published on their website. The dataset reports fishing activity in the Indian Ocean from January 1997 to December 2012. From this dataset, we selected only the long trail purse seine activities and aggregated the corresponding Yellowfin tuna catch reports. The following analyses have been obtained by using the D4ScienceAn e-Infrastructure operated by the D4Science.org initiative. Statistical Manager.
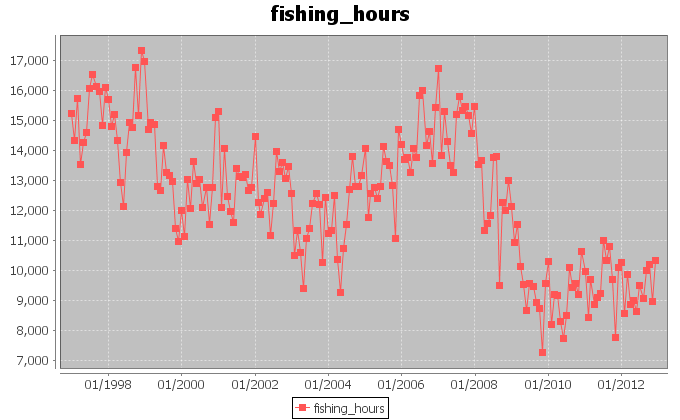
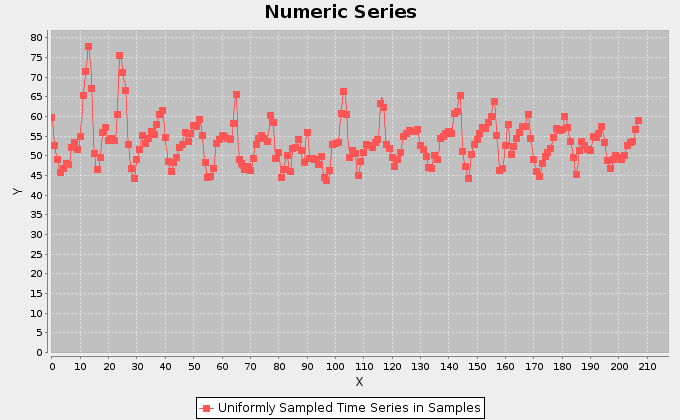
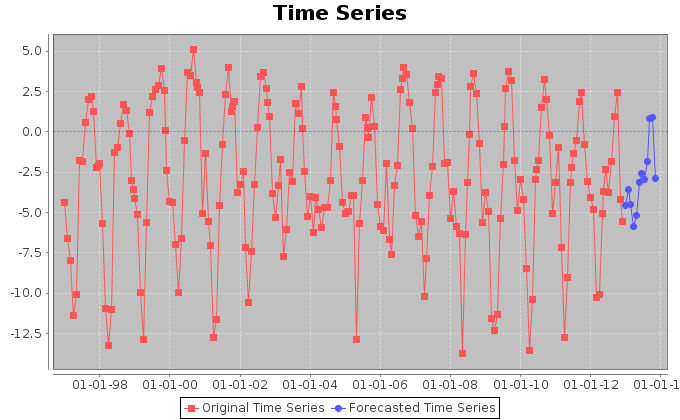
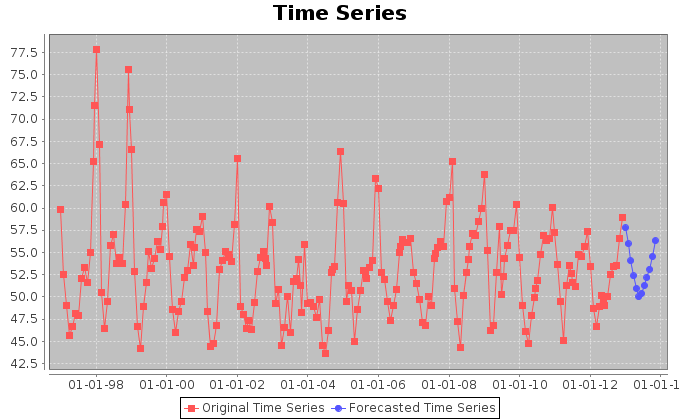
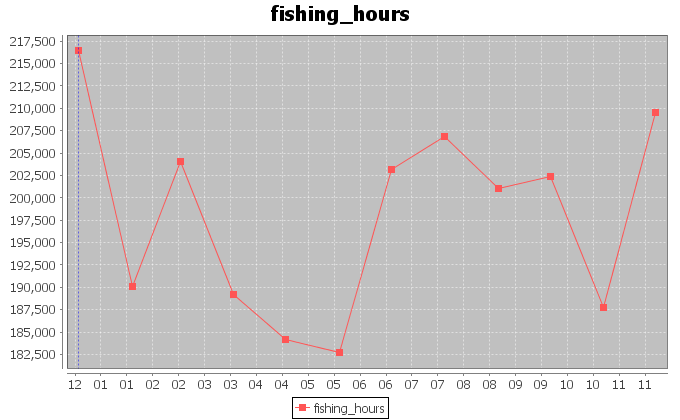
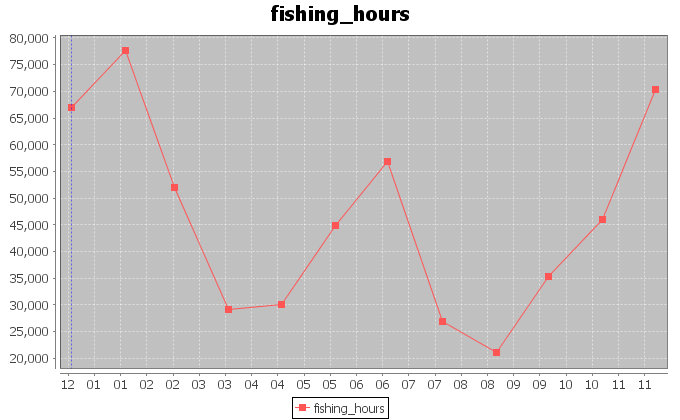
Our first analysis aimed at discovering hidden periodicities in the exploitation of the ocean area. Thus, we extracted the trend of the fishing hours effort in the period between January 1997 and December 2012. We summed the monthly hours spent by superposing reports and eventually obtained the above trend. We associated the total fishing hours for one month to the barycenter of the areas interested by the fishing activity in that month. The monthly barycenters were calculated by weighting each 1 degree cell in the original dataset, with the fishing hours spent in that month inside the cell. The complete resulting dataset can be found here. This contains unfolded information about the barycenters coordinates and their distances from the origin of the reference system.
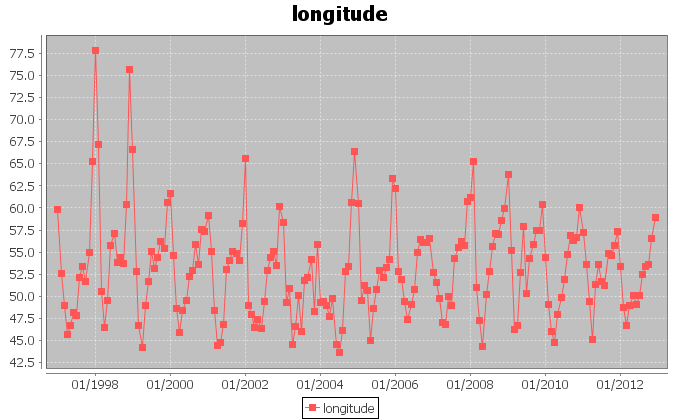
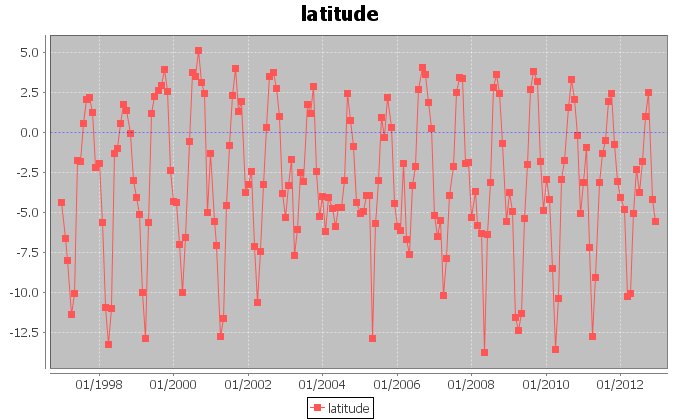
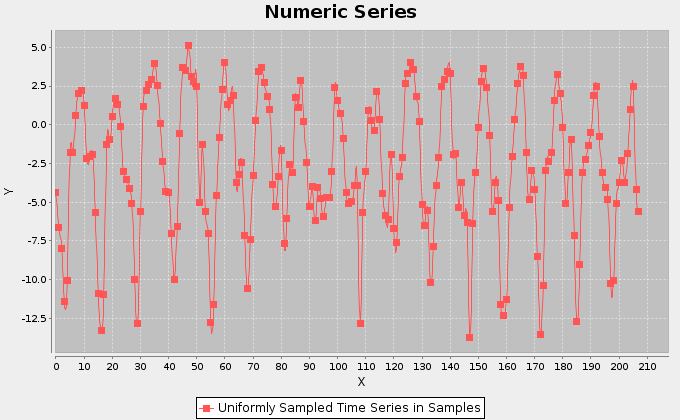
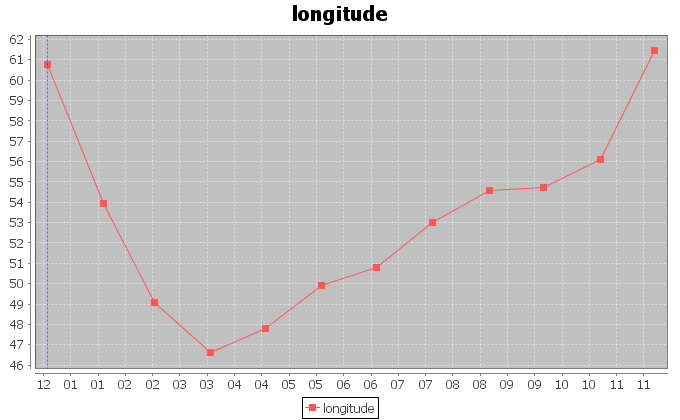
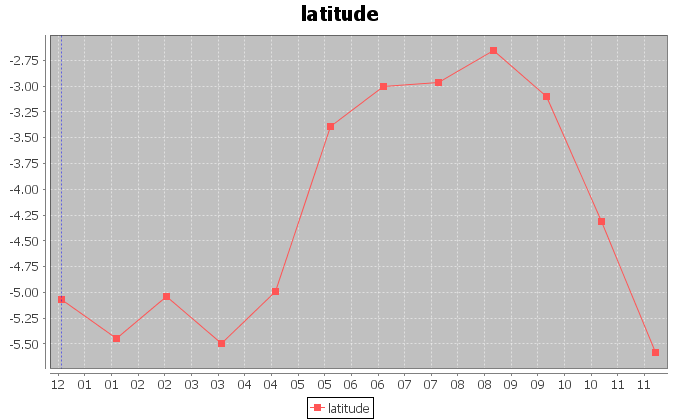
The figures above display the trends for the longitudes and latitudes of the monthly barycenters. The signals show a periodic behaviour, which we investigate more accurately later in this page.
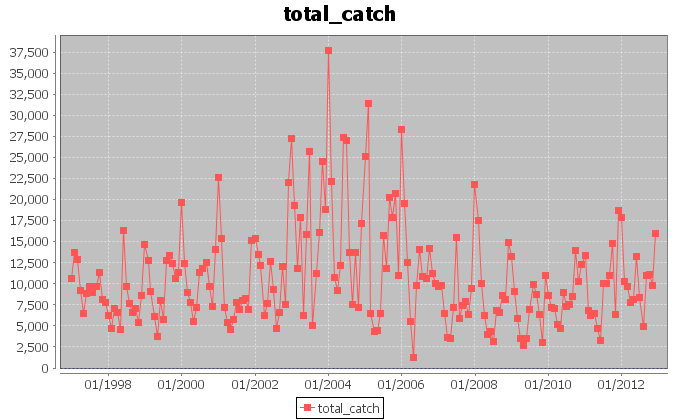
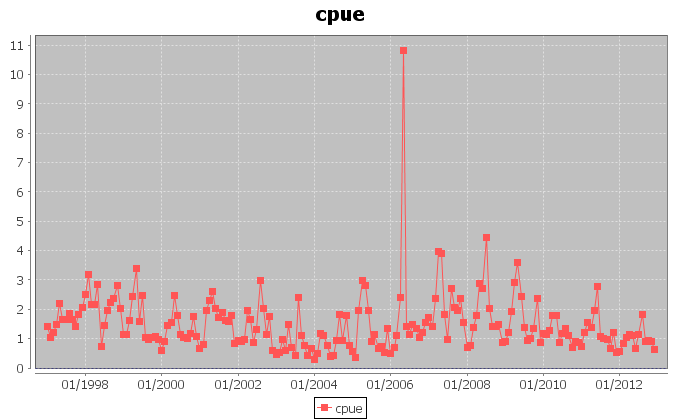
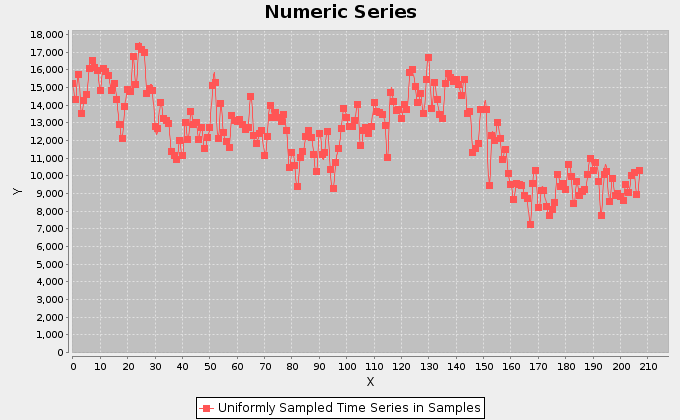
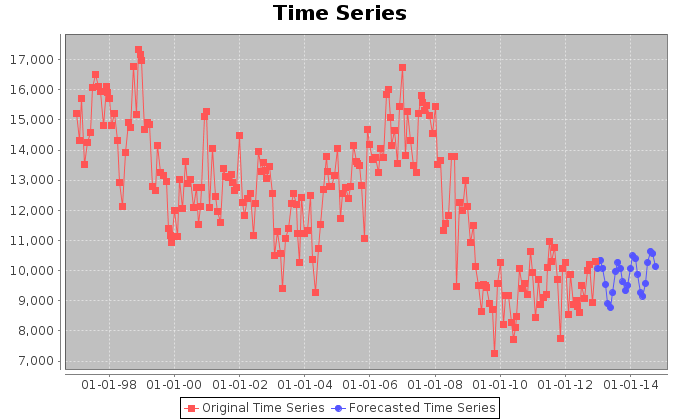
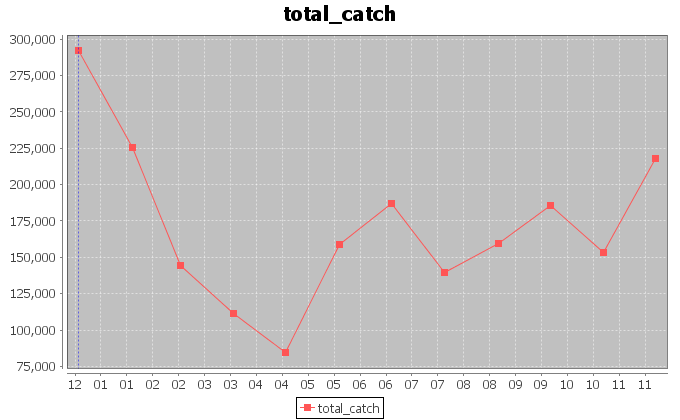
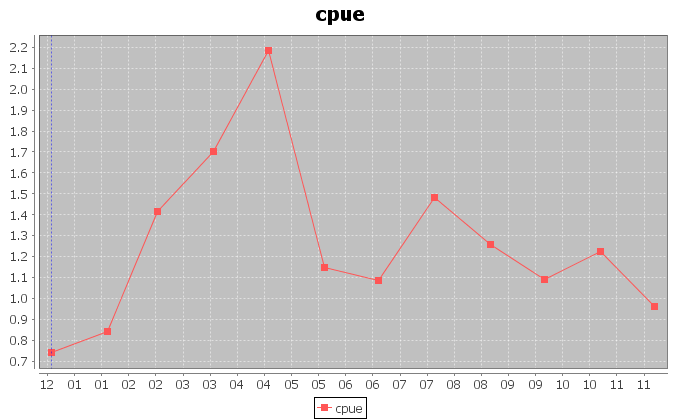
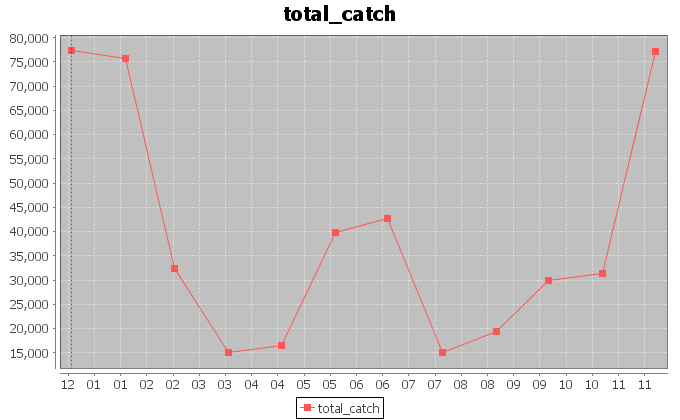
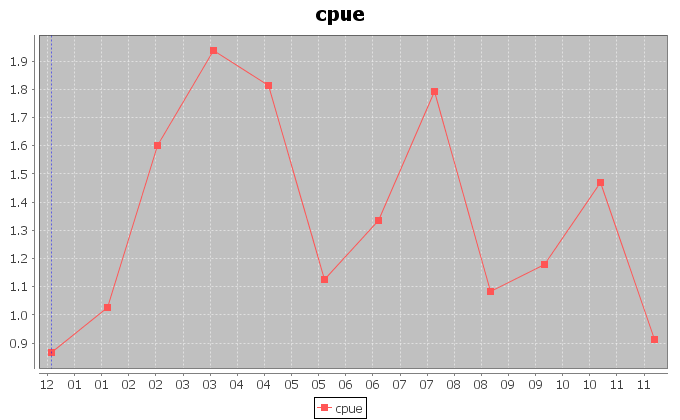
The above figures, instead, report the trends for the amount of catch in tonnes for the Yellowfin Tuna, and the related catch per unit of effort (CPUE) calculated as the ratio between the catch and the fishing hours.
In order to inspect the periodic behaviour of the trends of the coordinates, we applied Fourier analysis to the signals and traced spectrograms. For both longitude and latitude, the analysis detected a period of 51.0 samples with indecision interval [56.64 ; 46.38]. This corresponds to a periodic exploitation of areas after approximately 51 months.
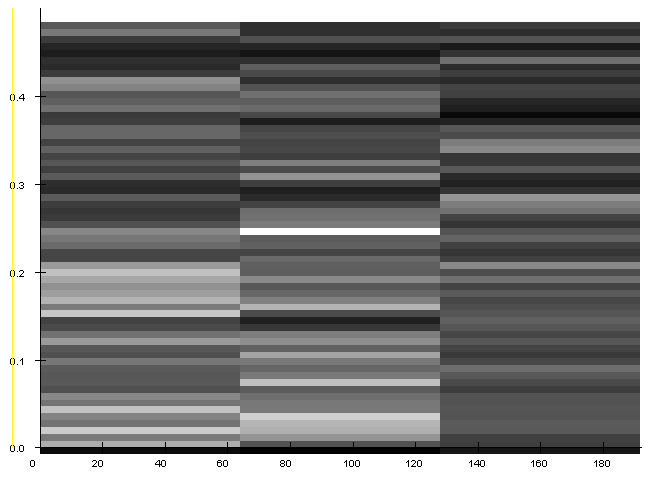
Fishing effort in hours, instead, is not a stationary signal, thus we tried to inspect its hidden periodicities by means of a Short-Time Fourier analysis. The analysis was made on 3 chunks of the signal presenting quite stationary means and variances. The analysis detected a weak overall periodicity of 12.91 samples with indecision interval between 13.25 and 12.59 samples. This indicates an annual periodicity in the variation of the fishing effort.
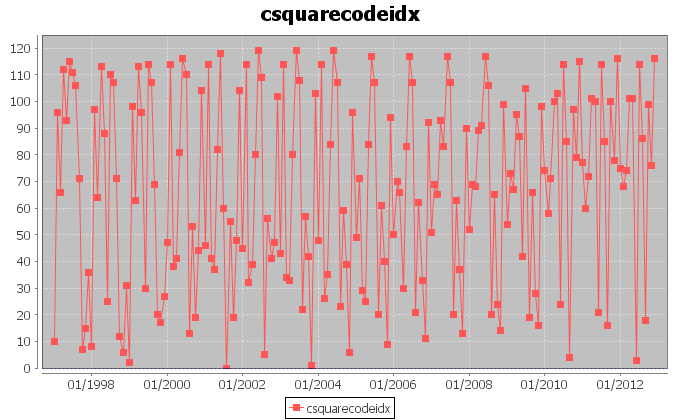
We also report the trend of the Csquare codes associated to the barycenters. Each code was assigned to an index and the above chart displays the distribution of such indexes in time. We adopted this representation in order to report a bidimensional phenomenon on one dimension. The trend of the indexes is periodic and this is due to the periodic trend in longitudes and latitudes.
Finally, we tried to forecast the coordinates trends in order to understand which places could be interested by exploitation in the 12 following months. To such aim, we used Singular Spectrum Analysis. The forecasts confirm the periodic nature of the coordinates signals. Furthermore, the forecast of the fishing hours effort, suggests that the amount of hours per month is going to oscillate around lower and lower values in average. Thus, the effort in purse seine is likely to be reduced.
Aggregation on 12 Months
We repeated the previous analysis, this time aggregating the fishing hours on 12 months. The figures above display the trends we extracted after the aggregation. The periodic nature of the fishing activity is no more visible, except for the latitudes of the barycenters. For this signal, a periodic behaviour of 12 months is visible, which demonstrates that the latitude periodic behaviour is stronger for latitude than for longitude.
Analysis on the Most Exploited Csquare
| Csquare code | Square Center (lat,lon) | Exploitation (fishing hours) |
|---|---|---|
| 1005 | (5;55) | 709254.3 |
| 3005 | (-5;55) | 614135.3 |
| 3004 | (-5;45) | 513798.8 |
| 3006 | (-5;65) | 258669.6 |
| 3104 | (-15;55) | 211621.1 |
| 3007 | (-5;75) | 33038.7 |
| 3105 | (-15;65) | 24718.3 |
| 1004 | (5;45) | 12235.1 |
As last analysis, we investigated the exploitation of the areas involved in the catch. We selected a coarse granularity of 10 degrees and ranked the most exploited square areas at this resolution. The trends and the data for each single square can be found here. The above table lists the most exploited squares, in Csquare encoding.
In the case of the secondmost exploited area, a periodic trend of 3\4 months is visible in the CPUE chart. The chart also shows that the catch per effort is lower and lower. This scenario indicates that higher catch has been obtained with less hours of fishing, during the last years.