CodelistManagerDesign
Context
Architecture
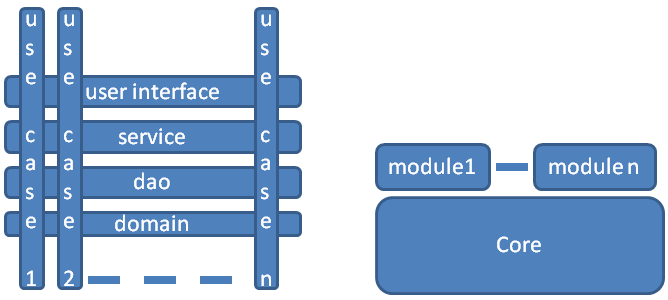
The core defines a basic user interface, the core services, core daos and the core domain objects. The core UI definitions define probably also the Menu. The core implements the core usecases.
Another starting point could be to say that the core has only domain objects, daos and services, so no UI definitions. This is still to be discussed and to be decided.
Every module covers 1 or more use cases. A module has usually a lot of UI definitions, and may add services, daos and domain objects.
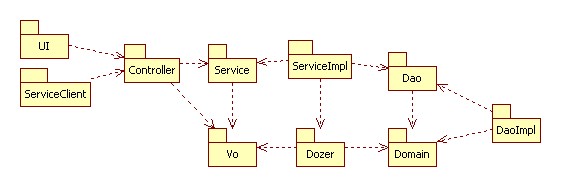
Package Diagram
Dozer is a utility to define mappings between object graphs. It has been explicitly modeled here in order to express that very responsibility.
Requirements
- DAO pattern is necessary in order to abstract from persistence implementations
- Identified persistence implementations are Oracle, Postgres, D4ScienceTreeManager, D4ScienceTabularDataManager
Questions
- Do the VOs in the Service interfaces need to interfaces or classes?
- Will the DAO have VOVirtual Organization;'s as wel in the interface, or domain objects?
Module Architecture
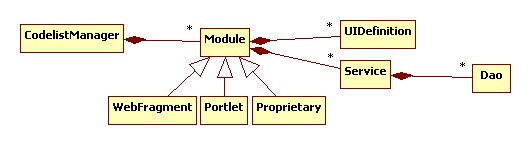
An instance of a CodelistManager can be deployed on a Java application server. A module can be packaged in a Custom, Porlet of WebFragment way.
Proprietary
The CodelistManager will have its own definitions of the notion of a module. Geoserver has done something similair. Every module is a jar file, can be dropped on the classpath and will add definitions to the UI menu. Geoserver has used intensively the Spring framework in order to implement its modularity.
Portlet
Packaging as portlet means complying with the Java Portlet Specification 2.0 (JSR 286). The portlets can be deployed on a portal server like http://www.liferay.com
WebFragment
Servlet 3.0 introduces web fragments. Every module can be packaged as a webfragement. http://java.sun.com/developer/technicalArticles/JavaEE/JavaEE6Overview_Part2.html
WebFramework
D4ScienceAn e-Infrastructure operated by the D4Science.org initiative. and TechCDR are using GWT. Other options are?
Dependency Injection
The options are Spring and Java 6 EE CDI[1].
Pros and cons
- The team is familiar with Spring.
- Fact is that CDI is having equal DI features as Spring and therefore Spring could be considered as a burden?
- Can caching be done as easy as in Spring through @Cacheable annotations?