Difference between revisions of "CodelistManager"
(→Workflow of an artefact) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Domain Model= | =Domain Model= | ||
| + | This is work in progress and has very much draft status. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Core== | ==Core== | ||
[[image:CoreDomainModel.jpg]] | [[image:CoreDomainModel.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 12 April 2012
Domain Model
This is work in progress and has very much draft status.
Core
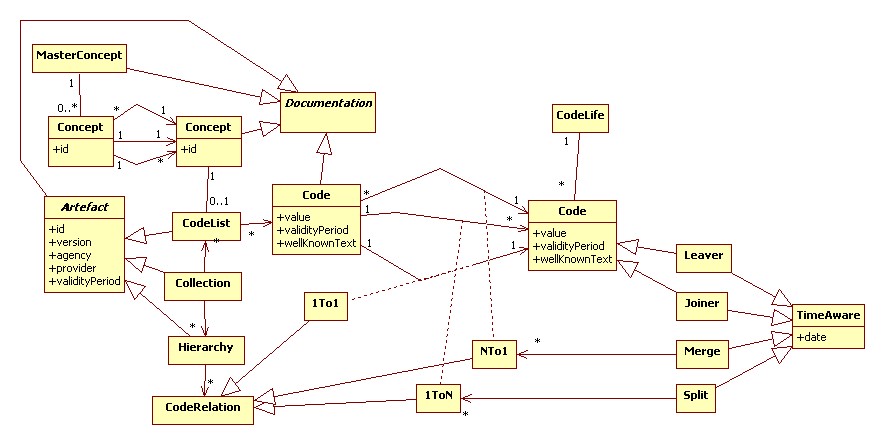 TODO: Leave, Joine and Merge need to be modeled better.
TODO: Leave, Joine and Merge need to be modeled better.
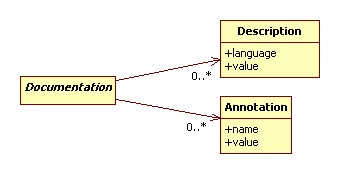
Documentation
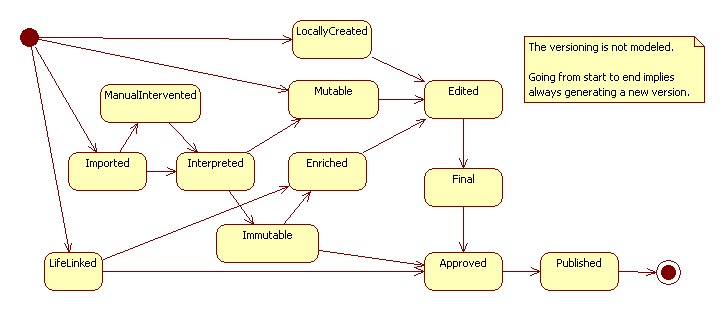
Workflow of an artefact
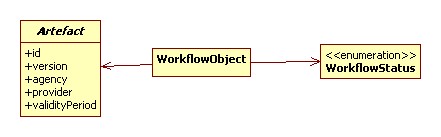
The WorkflowStatus has as possible values the possible artefact states.
Note that the workflow is aware of an artefact, not the other way around. Doing so, the workflow can be a pluggable module.
| Type (Artefact or Code) | Description |
| LocallyCreated | This is the default type. Created or imported and the further lifecycle and management is in the system |
| ImportedImmutable | Imported from outside and cannot be changed. Will have a CodeLife. The lifecycle and management is outside of the system but will be followed and monitored in the system. |
| LifeLinked | Is only linked, not stored and at most cached. Works in principle only in case the outside link is available. Will not have a CodeLife, the lifecycle and management is outside of the system |
Statechart of a Code
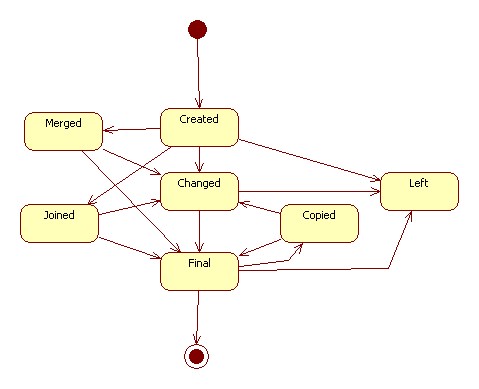 The CodeStatus has as values the possible code states.
The CodeStatus has as values the possible code states. 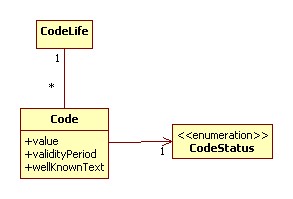
- A code can become final when:
- it is published in a codelist
- it is made final
- A code becomes non final when it was final and has been changed
- A code is non final when it is created
- A code can only change from final to non-final when it was not yet published in a codelist
- Changing the validityPeriod, wellKnownText or value of a final code will result in a copy of that code. The new code will be non final.
- Creating a new Code means also creating a new CodeLife
- Making a copy of a Code results in adding a link from that new Code to its CodeLife
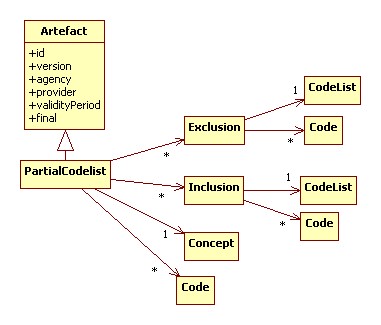
PartialCodelist
Use Cases
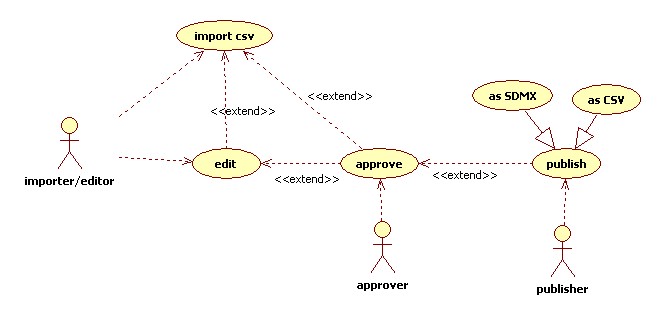
UseCase import csv
A good example for the import csv file is the ASFIS species list. The Asfis species list is a zip file, containing the file ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt, which is a csv file. The implicit hierarchies in this file are documented here. http://www.fao.org/fishery/collection/asfis/en documented here http://km.fao.org/FIGISwiki/index.php/ASFIS_SDMX_Codelist
After having imported the ASFIS file, the following codelists are interpreted:
- ASFIS Species Alpha 3 Codelist
- ASFIS Species Taxonomic Codelist
- ASFIS Species Family Taxonomic codelist
- ASFIS Species Order Taxonomic codelist
and hierarchies:
- Relation ASFIS Species Taxonomic code - Alpha 3 code
- Relation ASFIS Family - Species
- Relation ASFIS Order - Family
and collections
- ASFIS List of Species
Interpreted means that the system is capable of understanding all the implicit relations in the tabular format file like the the ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt file and shows in the UI distinguished codelists, hierarchies and collections. The ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt file results therefore in 4 codelits, 3 hierarchies and 1 collection.
The collection ASFIS List of Species is containing the same information as the original ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt file.
UseCase create new version of an Artefact
- Start from scratch, import, or copy an existing Artefact in order to work on a new version of an Artefact.
- Delete codes/hierarchies
- Add codes/hierarchies
- Edit codes/hierarchies
- View deleted codes/hierarchies
- View added codes/hierarchies
- View edited codes/hierarchies
- Make Artefact final
UseCase approve
A collection, codelist, hierarchy is approved and is ready to be published.
UseCase publish
A Collection, Codelist or Hierarchy can be published through SDMX, CSV:
- Codelists are published as SDMX codelists according the SDMX REST specifications.
- Hierarchies are published as SDMX hierarchical codelists according the SDMX REST specifications
- Collections are published as zip, txt, zip containing a txt file or zip containing a csv file. Such a collection would represent for instance the original ASFIS txt file.
UseCase publish geospatial referenced codelist
When codes have a geospatial reference through the attribute wellKnownText, it can be exported/published as a layer/WFSWeb Feature Service. Details of this usecase need to be refined further.
UseCase DiffReport
- User select artefact(Codelist, HierarchicalCodelist or Collection).
- User selects a certain version from that artefact.
- User selects another version from that same artefact.
- User clicks on generate DiffReport and views the DiffReport
The report shows:
- Codes added.
- Codes deleted.
- Number of codes in the first and second selected version.
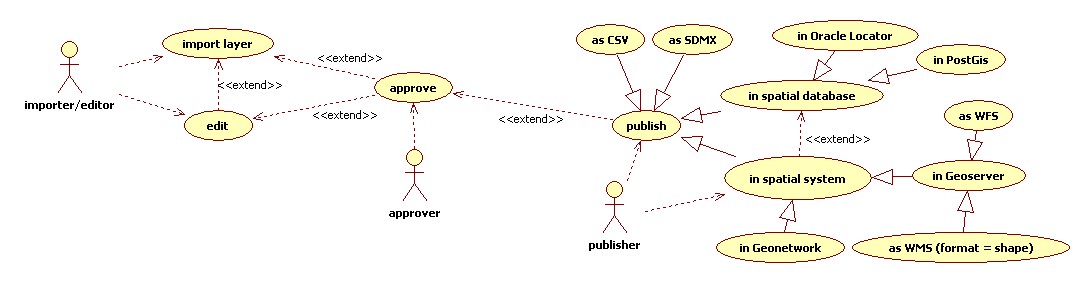
UseCase Import Layer
- Import layer (shapefile)
- .... process generic edit and approve functions
- Publish as WFSWeb Feature Service, CSV, SDMX, WMSSee Workload Management System or Web Mapping Service.(format shape)
- Publish in PostGis
- Publish in Oracle Locator
The practical case behind this usecase is the FAO major areas:
http://km.fao.org/FIGISwiki/index.php/FMA_SDMX_Codelist
After having imported the FAO areas layer, the following codelists are interpreted:
- FAO Production Area codelist (from major area to sub-unit)
- FAO Major Water Area codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Subarea codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Division codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Subdivision codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Subunit codelist
and hierarchies:
- Relation Area code - Subarea code
- Relation Subarea code - Division code
- Relation Division code - Subdivision code
- Relation Subdivision code - Subunit code
Rules
- The geometry is expressed as Well-known text(WKT) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Well-known_text
- Language dependent attributes from the shapefile are expressed as descriptions
- Non language dependent attributes from the shapefile are expressed as annotations
Core Rules
- A code can become final when:
- it is published in a codelist
- it is made final
- A code becomes non final when it was final and has been changed
- A code is non final when it is created
- A code can only change from final to non-final when it was not yet published in a codelist
- Changing the validityPeriod, wellKnownText or value of a final code will result in a copy of that code. The new code will be non final.
- Creating a new Code means also creating a new CodeLife
- Making a copy of a Code results in adding a link from that new Code to its CodeLife
Note: This table is not yet integrated in the model.
Nice to haves
- Integration with SharePoint
- Support for CMIS
- Export to OWL
- Export to SKOSS
- Export to RDF
- Merging
- Mapping
Links
[1]TaxoTools