Difference between revisions of "X-Link"
(→Design (tentative)) |
(→Design (tentative)) |
||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
=Design (tentative)= | =Design (tentative)= | ||
| − | + | We propose to start from a software library | |
| − | + | (in future one could easily use it to provide a web service, or any other user interface, gcube-related or not gcube-related). | |
| − | + | A rough description follows: | |
| − | + | === Setup === | |
| − | + | At setup time the user defines the desired categories and entity lists. | |
| − | + | To add a category (type) of entities we have to provide: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
* a sparql endpoint, | * a sparql endpoint, | ||
| − | * the URI of the resource class (type), e.g. ''http://www.ecoscope.org/ontologies/ecosystems_def#shark'' | + | * the URI of the resource class (type), e.g. ''http://www.ecoscope.org/ontologies/ecosystems_def#shark'' (or a SPARQL query that returns the desired lists of entities URIs). |
When a new category of entities is added, '''X-Search-Link''' | When a new category of entities is added, '''X-Search-Link''' | ||
| − | i) stores the sparql endpoint | + | i) stores the sparql endpoint to use, |
ii) constructs a sparql template query which will be used for retrieving entities related to a string, and | ii) constructs a sparql template query which will be used for retrieving entities related to a string, and | ||
iii) stores a list of named entities belonging to the category (i.e. instances of the class) and for each entity one or more corresponding URI(s). | iii) stores a list of named entities belonging to the category (i.e. instances of the class) and for each entity one or more corresponding URI(s). | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | === Input === | ||
| + | |||
| + | To apply its functionality over a particular document the user has to specify: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * the '''document''' he wants to analyze (e.g. pdf, doc, rdf, xml, web page, etc) | ||
| + | |||
| + | * the '''categories of entities''' for which he wants to detect entities in the document (e.g. Countries, Species, Water Areas, etc, or all possible categories), subset of the categories defined at startup. | ||
===Output=== | ===Output=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | The '''desired result''' is a list of entities, each described by a name and one or more URI(s). | |
| − | ( | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | A detailed possible specification (classes and method signatures), plus an example of how a client could use it, is given in the following file:... | ||
| + | |||
| + | We estimate that, a first implementation of the above specification, will require around 1.5PM. | ||
| + | |||
===Possible Implementations=== | ===Possible Implementations=== | ||
Revision as of 15:05, 3 April 2013
General Description
Persons responsible for editing/maintaining this page
- Pavlos Fafalios (fafalios@ics.forth.gr)
- Yannis Marketakis (marketak@ics.forth.gr)
- Julien Barde (julien.barde@ird.fr)
Description
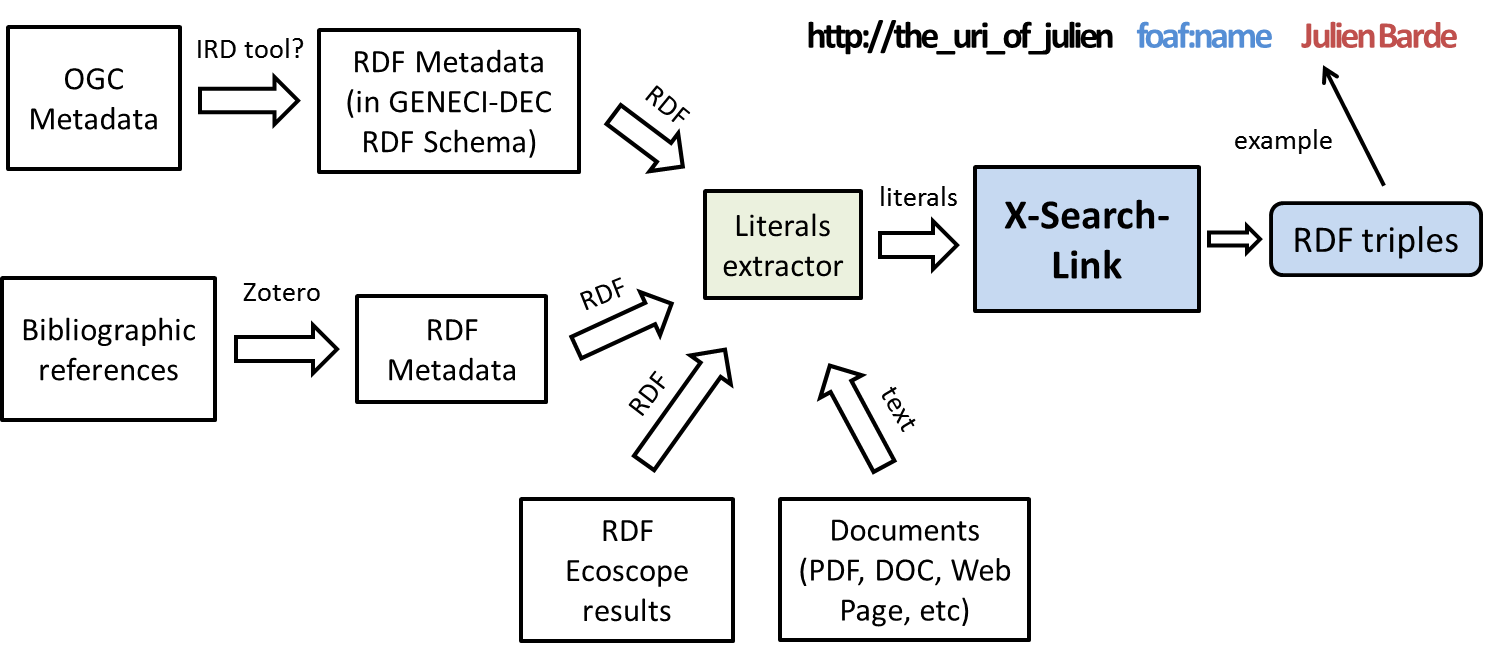
The requirements concern the development of an application (library? RESTful service? ..?) that, based on a knowledge base, will be able to match named entities that lie in a file to URIs. The objective is to rely upon previous demonstrations of entity mining (highlighting terms in web pages) to fit some needs of the community of users that will create new linked open data available for different clients (e.g. search engines). Among data to be turn into linked data: bibliographic references, metadata (OGC from geospatial cluster, RDF results from opensearch complying with GENESI-DEC RDF schema), named entities in documents (Word, PDF files), etc.
In brief, the aforementioned application should:
a) read the content of a file (doc/pdf/XML/RDF) or web page as input,
b) discover named entities of interest (e.g. keywords, Species, Persons, Organizations, etc.) in that file,
c) match each discovered entity with one (ideally) or more entities from the underlying knowledge bases (i.e. URIs of TLO, FLOD, Ecoscope, etc)
The supposed process is sketched in the following figure:
Examples:
1) From following author description:
<foaf:Person>
<foaf:givenname>C.</foaf:givenname>
<foaf:surname>Mellon-Duval</foaf:surname>
</foaf:Person>
The tagger will find the triple of the related foaf:agent in Ecoscope SPARQL enpoint (or other endpoints):
http://www.ecoscope.org/ontologies/agents/capucineMellon foaf:name C.Mellon-Duval
2) From the following:
<dc:subject>
<z:AutomaticTag>
<rdf:value>Mediterranean</rdf:value>
</z:AutomaticTag>
</dc:subject>
The tagger will find the triple of the related ecosystem in Ecoscope SPARQL enpoint (or other endpoints):
http://www.ecoscope.org/ontologies/ecosystems/mediterranean_ecosystem rdfs:label Mediterranean
Difficulties/Challenges:
a) We must limit the probability of erroneous matchings “Entity-URI”. Possible Solution: a user will approve the matchings (however this may be laborious), or only URIs without ambiguity will be kept.
b) If for an entity we have matched more than one possible URIs, which one to select? Possible Solution: a user will select the right one (however this may be laborious).
Related iMarine WP/Tasks
It could be considered related to T10.4 - Semantic Data Analysis Facilities although it was not described in the corresponding milestone: Semantic_Data_Analysis
Related iMarine Deliverables
-
Related Milestones
-
Related Cluster
http://wiki.i-marine.eu/index.php/Semantic_cluster_achievements
Related Presentations/Tutorials
-
Current (development) status
Understand the problem and define the requirements against the challenges.
Demo Scenarios
(to describe one or more ideal scenarios)
The following figure (by Julien) depicts a possible application that exploits the functionality of X-Search-Link:
Design (tentative)
We propose to start from a software library (in future one could easily use it to provide a web service, or any other user interface, gcube-related or not gcube-related).
A rough description follows:
Setup
At setup time the user defines the desired categories and entity lists. To add a category (type) of entities we have to provide:
- a sparql endpoint,
- the URI of the resource class (type), e.g. http://www.ecoscope.org/ontologies/ecosystems_def#shark (or a SPARQL query that returns the desired lists of entities URIs).
When a new category of entities is added, X-Search-Link i) stores the sparql endpoint to use, ii) constructs a sparql template query which will be used for retrieving entities related to a string, and iii) stores a list of named entities belonging to the category (i.e. instances of the class) and for each entity one or more corresponding URI(s).
Input
To apply its functionality over a particular document the user has to specify:
- the document he wants to analyze (e.g. pdf, doc, rdf, xml, web page, etc)
- the categories of entities for which he wants to detect entities in the document (e.g. Countries, Species, Water Areas, etc, or all possible categories), subset of the categories defined at startup.
Output
The desired result is a list of entities, each described by a name and one or more URI(s).
A detailed possible specification (classes and method signatures), plus an example of how a client could use it, is given in the following file:...
We estimate that, a first implementation of the above specification, will require around 1.5PM.
Possible Implementations
- Option A: Software Library
- Option B: Web ServiceSelf-contained, self-describing, modular application that can be published, located, and invoked across the Web. Web services perform functions that can be anything from simple requests to complicated business processes. Once a Web service is deployed, other applications (and other Web services) can discover and invoke the deployed service., e.g. RESTful API (this option requires the Software Library).
Given the above (Software Library and/or Web ServiceSelf-contained, self-describing, modular application that can be published, located, and invoked across the Web. Web services perform functions that can be anything from simple requests to complicated business processes. Once a Web service is deployed, other applications (and other Web services) can discover and invoke the deployed service.), one could develop a Portlet which will exploit X-Search-Link for offering any kind of desired functionality.
Plans and Next Steps
A tentative plan is to:
a) understand the problem and define the requirements against the challenges (by end of Feb 2013),
b) decide what is required to be designed/implemented (by end of Apr 2013), and
c) have a first implementation.
Related Tickets
Requirements
Enriching RDF files with the URIs of Named Entities (#1187)
Design
-
Implementation
-