Difference between revisions of "YASMEEN"
(→CLI tools) |
(→PROCESS MATCHING RESULTS) |
||
| (59 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | "''Yet Another Species Matching Execution | + | "''Yet Another Species Matching Execution ENvironment''" |
== Purposes == | == Purposes == | ||
| − | YASMEEN is a set of data formats, reference data files and tools to perform species names matching identification between a set of input data and multiple reference data sets. | + | YASMEEN (''Yet Another Species Matching Execution ENvironment'') is a set of [[YASMEEN data formats|data formats]], [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Reference_data_download|reference data files]] and [[#CLI tools|tools]] to perform species names matching identification between a set of input data and multiple reference data sets. |
| − | The matching process can be configured to include and combine a set of ''matchlets'', each dealing with specific attributes of the species data model. Each matchlet will in turn produce a matching score according to its nature and to the actual values of the attributes being compared between each input data and reference data pair. | + | The matching process can be configured to include and combine a set of ''matchlets'', each dealing with specific attributes of the [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Object_data_model|species data model]]. Each matchlet will in turn produce a matching score according to its nature and to the actual values of the attributes being compared between each input data and reference data pair. |
Matchlets can be assigned different weights and minimum score thresholds: the overall matching score for an input / reference data pair, according to the configured matchlets, will be the weighted value of each triggered matchlet's score. | Matchlets can be assigned different weights and minimum score thresholds: the overall matching score for an input / reference data pair, according to the configured matchlets, will be the weighted value of each triggered matchlet's score. | ||
| − | Furthermore, existing matchlets dealing with ''string''-like attributes (e.g. scientific names, kingdom, genus, authors etc.) are configured out of the box so as to use a combination of well-established lexical measures | + | Furthermore, existing matchlets dealing with ''string''-like attributes (e.g. scientific names, kingdom, genus, authors etc.) are configured out of the box so as to use a combination of well-established [[YASMEEN_lexical_measures|lexical measures]] that will in turn be used to produce the matchlet's final score for a given pair of input / reference data attributes. |
Matchlets do already exist that deal with any of the species data model attribute and implement many a different matching algorithm (Tony Rees' Taxamatch, GSAy and others). Additionally, new matchlets can be designed and plugged in the system to allow for easy incorporation of new matching strategies. | Matchlets do already exist that deal with any of the species data model attribute and implement many a different matching algorithm (Tony Rees' Taxamatch, GSAy and others). Additionally, new matchlets can be designed and plugged in the system to allow for easy incorporation of new matching strategies. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
YASMEEN is based upon FAO's COMET (COncept Matching Engine and Tools) an open-source framework designed to model and support generic data matching processes, of which it is a specialization in the domain of species data. YASMEEN shares and extends the COMET core data model and matching engine, as well as the matching result output format (XML) thus being able to take advantage of any additional, general purpose tool developed for the original framework. | YASMEEN is based upon FAO's COMET (COncept Matching Engine and Tools) an open-source framework designed to model and support generic data matching processes, of which it is a specialization in the domain of species data. YASMEEN shares and extends the COMET core data model and matching engine, as well as the matching result output format (XML) thus being able to take advantage of any additional, general purpose tool developed for the original framework. | ||
| − | == | + | == Data flow == |
| − | YASMEEN | + | The YASMEEN data flow to perform matching identification of a set of input data against a set of reference data is as follows: |
| − | + | === PRODUCE REFERENCE DATA === | |
| + | A DWCA file is sent to the [[YASMEEN converter]] tool, that will in turn transform the DWCA file into two [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Reference_data_.28Taxon_Authority_File.29|TAF]] files (one for taxa data and one for vernacular names data) that can be later referenced by the matching engine in the [[#MATCH DATA|MATCH DATA]] step. '''''This preliminary step is optional''''', and is accounted for only when users want to produce a set of reference data from a newly available DWCA file (not included in the distributed set of TAF reference data) | ||
| − | + | === PRODUCE INPUT DATA === | |
| + | Input data are produced as a simple text file listing an input data entry per each line. Each input data entry can consist of a simple species name, a combination of species name and authority information or anything that came out of the original data provider. | ||
| − | + | Given the extremely variable nature of input data sources, no YASMEEN CLI tool exists that can implement this step: the input data production must be performed by external, custom tools (e.g. DB exports, CSV extractions, remote resources retrievements, user input etc.). | |
| + | |||
| + | In any case, the format of this file must adhere to the [[YASMEEN data formats#Raw input data|YASMEEN raw input data format]] | ||
| − | The | + | === PARSE INPUT DATA === |
| + | The input data file is processed by the [[YASMEEN input data parser]] tool, that in turn will produce a parsed version (according to the parser of choice) of the provided input data and also apply pre-parsing and post-parsing transformations. The produced output file will be in the [[YASMEEN data formats#Parsed input data|YASMEEN parsed input data format]] | ||
| − | + | === MATCH DATA === | |
| − | + | The parsed input data file (in the [[YASMEEN data formats#Parsed input data|YASMEEN parsed input data format]]) is sent to the [[YASMEEN matching engine]] tool, together with the specification of the reference data files to use (in [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Reference_data_.28Taxon_Authority_File.29|TAF]] format) and the chosen matchlets configuration | |
| − | + | ||
| − | === | + | === PRODUCE MATCHING RESULTS === |
| + | Matching results are produced and stored in one of the [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Output_data|formats]] of choice. The [[YASMEEN matching engine]] tool can produce the raw XML as per the COMET matching result output specification, a stripped and simplified version of this same XML as well as a CSV representation of the most meaningful output data per each result. Users can also specify their own XSLT file that will be applied to the raw XML output to produce the final result (in whatever format they like) | ||
| − | YASMEEN and | + | ==== PROCESS MATCHING RESULTS ==== |
| + | This is an optional phase in which multiple matching results (produced by separate runs of the [[YASMEEN matching engine]]) can be merged together and possibly filtered out by number of matching candidates and / or candidates matching score via the [[YASMEEN_matching_results_merger|YASMEEN matching results merger]]. Also, with the help of the [[YASMEEN_input-output_filter|YASMEEN input-output filter]] it is possible to build a new input data file (to be used in the [[#MATCH_DATA|MATCH DATA]] step) out of an initial parsed input data file and the matching results produced - for this same input file - by the [[YASMEEN matching engine]]. | ||
| − | + | These two sub-steps are particularly relevant in the context of an iterative matching workflow. | |
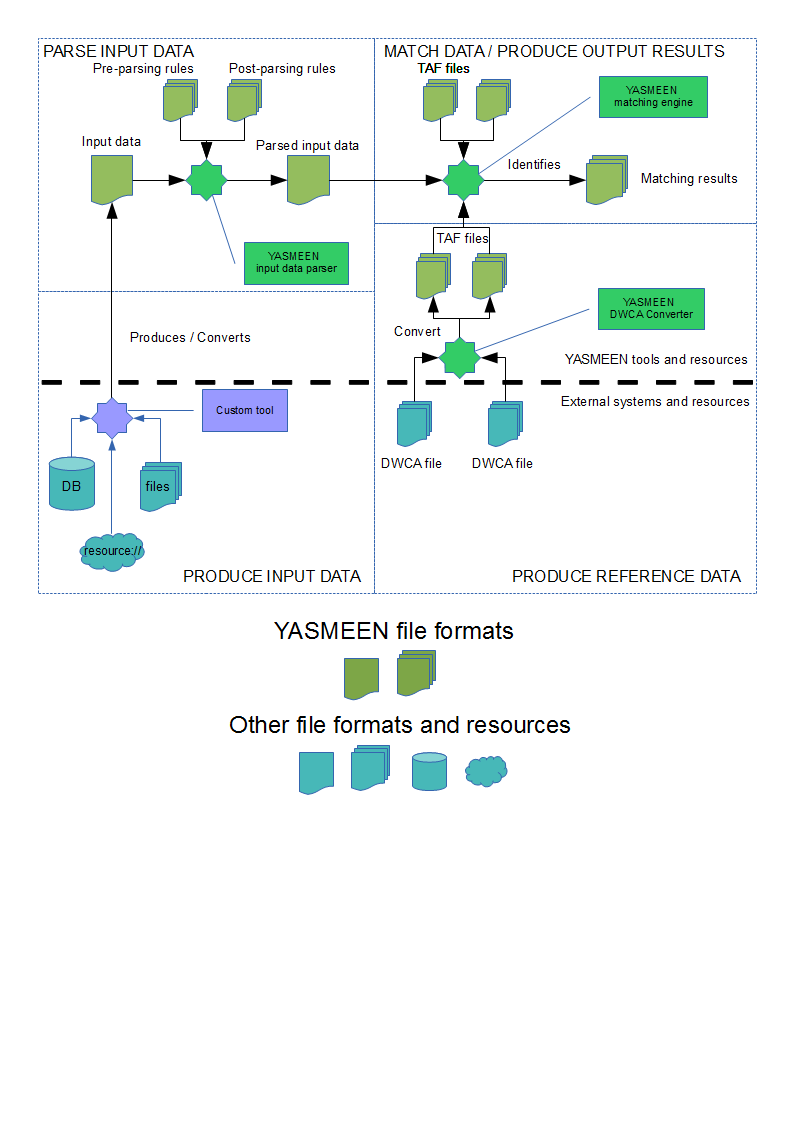
| − | == | + | == YASMEEN data flow boundaries and interactions == |
| − | + | [[File:YASMEEN_systems_interactions_and_boundaries.png]] | |
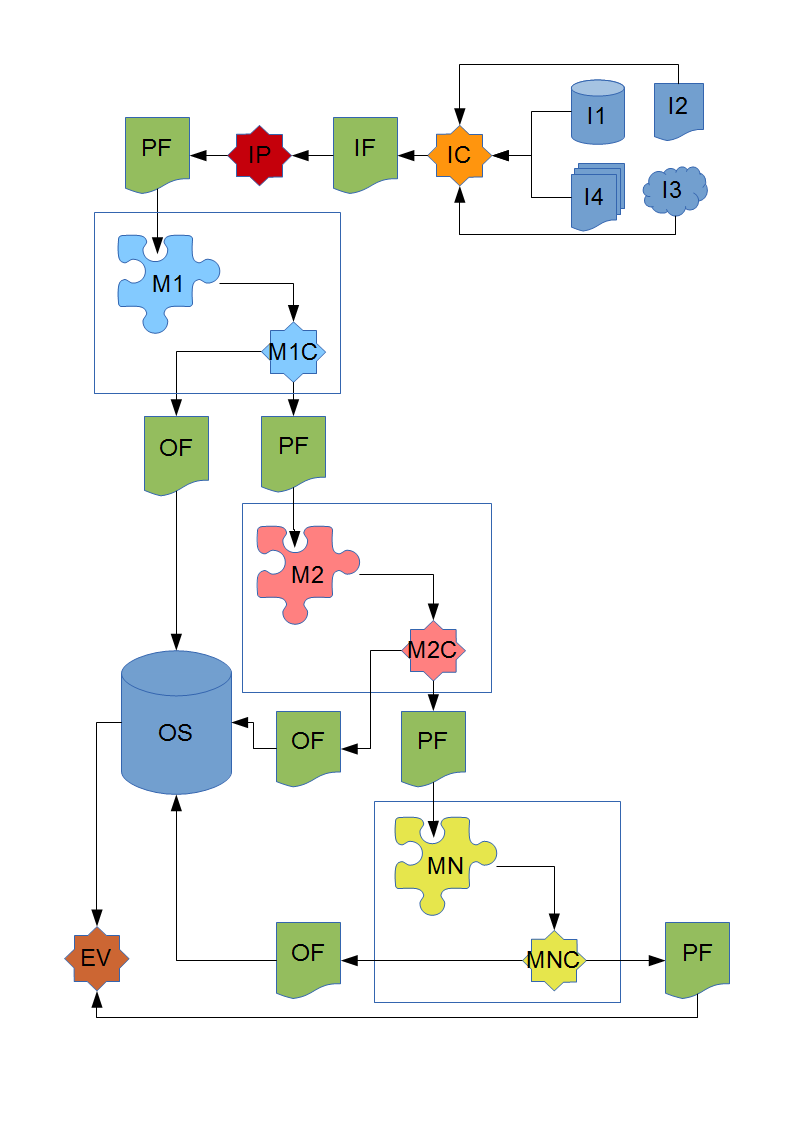
| − | + | == The BiOnym workflow == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[File:bionym.png]] | |
| − | + | YASMEEN can act as one ''matcher'' inside the biOnym workflow. Potentially, this workflow can use its own set of input / output data formats: as of today, the YASMEEN data formats are being evaluated as standard formats for the data interchange inside the biOnym workflow, at least at the level of inter-matchers data exchange. | |
| − | + | The depicted workflow has the following components: | |
| − | + | * '''I1, I2, I3, I4''': a set of input data sources in whatever format they are available (DB tables, files, documents, remote resources etc.) | |
| + | * '''IC''': an input converter that takes the input data and produces a version of these same data in the input format '''IF''' | ||
| + | * '''IP''': an input parser that takes converted input data (in '''IF''' format) and produces a parsed, pre-processed version in '''PF''' format | ||
| + | * '''M1''': a matcher (whatever its implementation) that takes parsed input data in '''PF''' format, performs the matching against its reference data set and produces matching results | ||
| + | * '''M1C''': a matching results converter, that takes the matching results out of '''M1''', sends valid matching to the output storage '''OS''' in '''OF''' format and passes non-matching results (converted in the '''PF''' format) to the next matcher in the chain | ||
| + | * '''M2''': a matcher (whatever its implementation) that takes the non-matching results from '''M1C''' (in '''PF''' format) performs the matching against its reference data set and produces matching results | ||
| + | * '''M2C''': a matching results converter, that takes the matching results out of '''M2''', sends valid matching to the output storage '''OS''' in '''OF''' format and passes non-matching results (converted in the '''PF''' format) to the next matcher in the chain | ||
| + | * '''MN''': a matcher (whatever its implementation) that takes the non-matching results from '''MN-1C''' (in '''PF''' format) performs the matching against its reference data set and produces matching results | ||
| + | * '''MNC''': a matching results converter, that takes the matching results out of '''M3''', sends valid matching to the output storage '''OS''' in '''OF''' format and returns non-matching results (converted in the '''PF''' format) as process output | ||
| + | * '''OS''': the output storage, that stores valid matching received from each matcher in the chain and provides stored matching results on request | ||
| + | * '''EV''': an evaluator component, that takes the stored valid matching results in '''OF''' format together with the output of '''MNC''' in '''PF''' format and provides support to human operators in the task of validating the outcomes of the process | ||
| − | + | Whether YASMEEN [[YASMEEN_data_formats|data formats]] are adopted as data formats of choice for the biOnym workflow or not, [[YASMEEN]] still can fulfill the role of any matcher in the chain. In the latter case, transducer components must be designed to convert from the chosen biOnym data formats to the YASMEEN [[YASMEEN_data_formats|data formats]]. In particular: | |
| − | + | * '''IF''' needs to be converted in the YASMEEN [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Raw_input_data|raw input data format]] | |
| + | * '''PF''' needs to be converted in the YASMEEN [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Parsed_input_data|parsed input data format]] | ||
| + | * the YASMEEN [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Output_data|output data]] format needs to be converted in the '''OF''' format. | ||
| − | + | Conversely, '''IF''', '''PF''' and '''OF''' will be mapped onto the YASMEEN [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Raw_input_data|raw input data format]], [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Parsed_input_data|parsed input data format]] and [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Output_data|output data format]] while '''IP''' will be directly implemented by the YASMEEN [[YASMEEN_input_data_parser|input data parser]]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == CLI tools == | |
| − | === | + | === System requirements === |
| − | + | YASMEEN and its CLI tools are written in Java, thus they can run on any machine and Operating System for which a JVM is available. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Java version 6 or higher is required: it is also recommended to run YASMEEN on a machine with at least 2GB of RAM and a dual core CPU. | |
| − | + | === Available tools === | |
| − | + | The current set of YASMEEN CLI tools includes: | |
| − | + | ==== The [[ YASMEEN converter ]] ==== | |
| − | + | that produces [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Reference_data_.28Taxon_Authority_File.29|TAF]] files out of DWCA files | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==== The [[ YASMEEN input data parser ]] ==== | |
| − | + | that parses, pre / post processes and converts raw input data in a format suitable for the matching process | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==== The [[ YASMEEN matching engine ]] ==== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | that compares parsed input data against a set of reference data (in [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Reference_data_.28Taxon_Authority_File.29|TAF]] format) according to a set of ''matchlets'' and produces a matching report for later evaluation. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==== The [[ YASMEEN matching results merger ]] ==== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | that allows merging (and optionally filtering) matching output results in raw (COMET) XML format. Particularly useful to produce the overall results out of partial results produced by distinct, parallel processes running on different machines (on the same ref. data). | |
| + | |||
| + | ==== The [[ YASMEEN input-output filter ]] ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | that allows identifying which input data has not produced any entry in a matching result output and thus re-process those data only, possibly with a different matching process configuration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Distribution == | ||
| + | |||
| + | YASMEEN is shipped as a set of command line tools plus a set of reference data sets compiled from currently available DarWin Core Archive (DWCA) files - for taxa and vernacular data - produced and made publicly available by third-party institutions and organizations (FAO / ASFIS, FISHBASE, OBIS, IRMNG, COL, WORMS etc.). | ||
| − | + | Potentially, any data set that comes (or can be converted) in DWCA format can be transformed by the [[YASMEEN converter]] tool into the expected ''Taxon Authority File'' format ([[YASMEEN_data_formats#Reference_data_.28Taxon_Authority_File.29|TAF]]) and used as a reference data set for the matching process. | |
| − | + | Reference data sets in [[YASMEEN_data_formats#Reference_data_.28Taxon_Authority_File.29|TAF]] format will be constantly kept updated and distributed separately from the command line tools. | |
Latest revision as of 09:48, 4 November 2013
"Yet Another Species Matching Execution ENvironment"
Purposes
YASMEEN (Yet Another Species Matching Execution ENvironment) is a set of data formats, reference data files and tools to perform species names matching identification between a set of input data and multiple reference data sets.
The matching process can be configured to include and combine a set of matchlets, each dealing with specific attributes of the species data model. Each matchlet will in turn produce a matching score according to its nature and to the actual values of the attributes being compared between each input data and reference data pair.
Matchlets can be assigned different weights and minimum score thresholds: the overall matching score for an input / reference data pair, according to the configured matchlets, will be the weighted value of each triggered matchlet's score.
Furthermore, existing matchlets dealing with string-like attributes (e.g. scientific names, kingdom, genus, authors etc.) are configured out of the box so as to use a combination of well-established lexical measures that will in turn be used to produce the matchlet's final score for a given pair of input / reference data attributes.
Matchlets do already exist that deal with any of the species data model attribute and implement many a different matching algorithm (Tony Rees' Taxamatch, GSAy and others). Additionally, new matchlets can be designed and plugged in the system to allow for easy incorporation of new matching strategies.
Background
YASMEEN is based upon FAO's COMET (COncept Matching Engine and Tools) an open-source framework designed to model and support generic data matching processes, of which it is a specialization in the domain of species data. YASMEEN shares and extends the COMET core data model and matching engine, as well as the matching result output format (XML) thus being able to take advantage of any additional, general purpose tool developed for the original framework.
Data flow
The YASMEEN data flow to perform matching identification of a set of input data against a set of reference data is as follows:
PRODUCE REFERENCE DATA
A DWCA file is sent to the YASMEEN converter tool, that will in turn transform the DWCA file into two TAF files (one for taxa data and one for vernacular names data) that can be later referenced by the matching engine in the MATCH DATA step. This preliminary step is optional, and is accounted for only when users want to produce a set of reference data from a newly available DWCA file (not included in the distributed set of TAF reference data)
PRODUCE INPUT DATA
Input data are produced as a simple text file listing an input data entry per each line. Each input data entry can consist of a simple species name, a combination of species name and authority information or anything that came out of the original data provider.
Given the extremely variable nature of input data sources, no YASMEEN CLI tool exists that can implement this step: the input data production must be performed by external, custom tools (e.g. DB exports, CSV extractions, remote resources retrievements, user input etc.).
In any case, the format of this file must adhere to the YASMEEN raw input data format
PARSE INPUT DATA
The input data file is processed by the YASMEEN input data parser tool, that in turn will produce a parsed version (according to the parser of choice) of the provided input data and also apply pre-parsing and post-parsing transformations. The produced output file will be in the YASMEEN parsed input data format
MATCH DATA
The parsed input data file (in the YASMEEN parsed input data format) is sent to the YASMEEN matching engine tool, together with the specification of the reference data files to use (in TAF format) and the chosen matchlets configuration
PRODUCE MATCHING RESULTS
Matching results are produced and stored in one of the formats of choice. The YASMEEN matching engine tool can produce the raw XML as per the COMET matching result output specification, a stripped and simplified version of this same XML as well as a CSV representation of the most meaningful output data per each result. Users can also specify their own XSLT file that will be applied to the raw XML output to produce the final result (in whatever format they like)
PROCESS MATCHING RESULTS
This is an optional phase in which multiple matching results (produced by separate runs of the YASMEEN matching engine) can be merged together and possibly filtered out by number of matching candidates and / or candidates matching score via the YASMEEN matching results merger. Also, with the help of the YASMEEN input-output filter it is possible to build a new input data file (to be used in the MATCH DATA step) out of an initial parsed input data file and the matching results produced - for this same input file - by the YASMEEN matching engine.
These two sub-steps are particularly relevant in the context of an iterative matching workflow.
YASMEEN data flow boundaries and interactions
The BiOnym workflow
YASMEEN can act as one matcher inside the biOnym workflow. Potentially, this workflow can use its own set of input / output data formats: as of today, the YASMEEN data formats are being evaluated as standard formats for the data interchange inside the biOnym workflow, at least at the level of inter-matchers data exchange.
The depicted workflow has the following components:
- I1, I2, I3, I4: a set of input data sources in whatever format they are available (DB tables, files, documents, remote resources etc.)
- IC: an input converter that takes the input data and produces a version of these same data in the input format IF
- IP: an input parser that takes converted input data (in IF format) and produces a parsed, pre-processed version in PF format
- M1: a matcher (whatever its implementation) that takes parsed input data in PF format, performs the matching against its reference data set and produces matching results
- M1C: a matching results converter, that takes the matching results out of M1, sends valid matching to the output storage OS in OF format and passes non-matching results (converted in the PF format) to the next matcher in the chain
- M2: a matcher (whatever its implementation) that takes the non-matching results from M1C (in PF format) performs the matching against its reference data set and produces matching results
- M2C: a matching results converter, that takes the matching results out of M2, sends valid matching to the output storage OS in OF format and passes non-matching results (converted in the PF format) to the next matcher in the chain
- MN: a matcher (whatever its implementation) that takes the non-matching results from MN-1C (in PF format) performs the matching against its reference data set and produces matching results
- MNC: a matching results converter, that takes the matching results out of M3, sends valid matching to the output storage OS in OF format and returns non-matching results (converted in the PF format) as process output
- OS: the output storage, that stores valid matching received from each matcher in the chain and provides stored matching results on request
- EV: an evaluator component, that takes the stored valid matching results in OF format together with the output of MNC in PF format and provides support to human operators in the task of validating the outcomes of the process
Whether YASMEEN data formats are adopted as data formats of choice for the biOnym workflow or not, YASMEEN still can fulfill the role of any matcher in the chain. In the latter case, transducer components must be designed to convert from the chosen biOnym data formats to the YASMEEN data formats. In particular:
- IF needs to be converted in the YASMEEN raw input data format
- PF needs to be converted in the YASMEEN parsed input data format
- the YASMEEN output data format needs to be converted in the OF format.
Conversely, IF, PF and OF will be mapped onto the YASMEEN raw input data format, parsed input data format and output data format while IP will be directly implemented by the YASMEEN input data parser.
CLI tools
System requirements
YASMEEN and its CLI tools are written in Java, thus they can run on any machine and Operating System for which a JVM is available.
Java version 6 or higher is required: it is also recommended to run YASMEEN on a machine with at least 2GB of RAM and a dual core CPU.
Available tools
The current set of YASMEEN CLI tools includes:
The YASMEEN converter
that produces TAF files out of DWCA files
The YASMEEN input data parser
that parses, pre / post processes and converts raw input data in a format suitable for the matching process
The YASMEEN matching engine
that compares parsed input data against a set of reference data (in TAF format) according to a set of matchlets and produces a matching report for later evaluation.
The YASMEEN matching results merger
that allows merging (and optionally filtering) matching output results in raw (COMET) XML format. Particularly useful to produce the overall results out of partial results produced by distinct, parallel processes running on different machines (on the same ref. data).
The YASMEEN input-output filter
that allows identifying which input data has not produced any entry in a matching result output and thus re-process those data only, possibly with a different matching process configuration.
Distribution
YASMEEN is shipped as a set of command line tools plus a set of reference data sets compiled from currently available DarWin Core Archive (DWCA) files - for taxa and vernacular data - produced and made publicly available by third-party institutions and organizations (FAO / ASFIS, FISHBASE, OBIS, IRMNG, COL, WORMS etc.).
Potentially, any data set that comes (or can be converted) in DWCA format can be transformed by the YASMEEN converter tool into the expected Taxon Authority File format (TAF) and used as a reference data set for the matching process.
Reference data sets in TAF format will be constantly kept updated and distributed separately from the command line tools.