Difference between revisions of "CodelistManager"
(→Domain Core) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Domain Model= | =Domain Model= | ||
| − | == | + | ==Core== |
[[image:CoreDomainModel.jpg]] | [[image:CoreDomainModel.jpg]] | ||
| − | TODO: Leave, Joine and Merge need to be modeled better. | + | TODO: Leave, Joine and Merge need to be modeled better. |
==Domain Multi language== | ==Domain Multi language== | ||
Revision as of 12:23, 12 April 2012
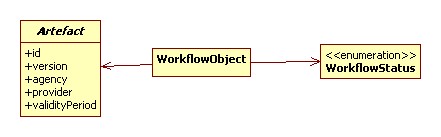
Domain Model
Core
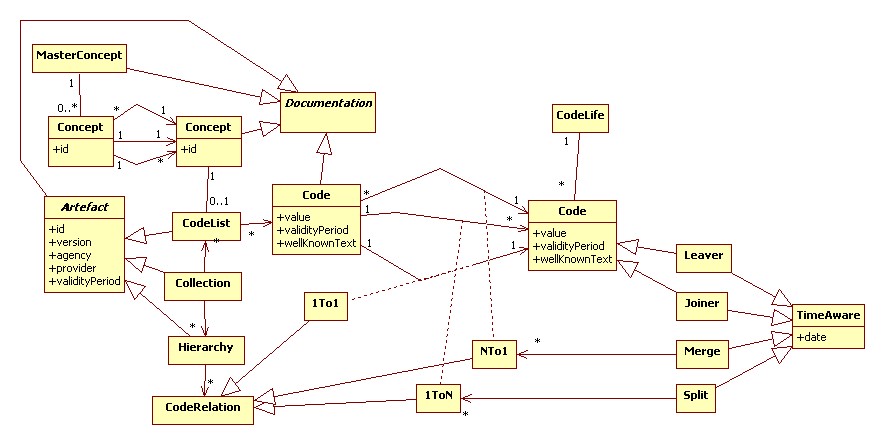 TODO: Leave, Joine and Merge need to be modeled better.
TODO: Leave, Joine and Merge need to be modeled better.
Domain Multi language
Domain Import
Domain Workflow
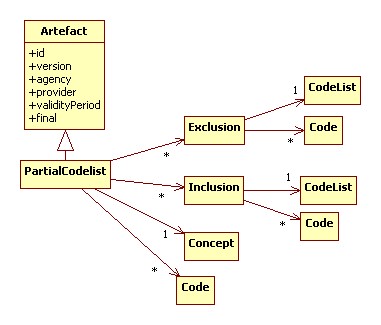
PartialCodelist
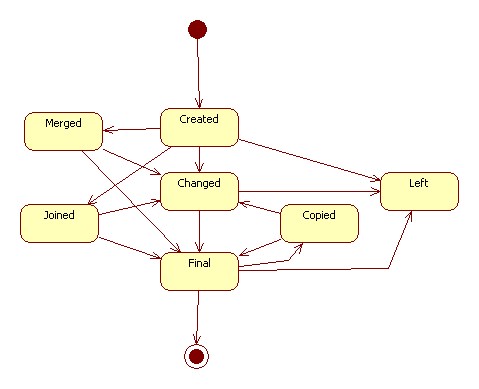
Statechart of a Code
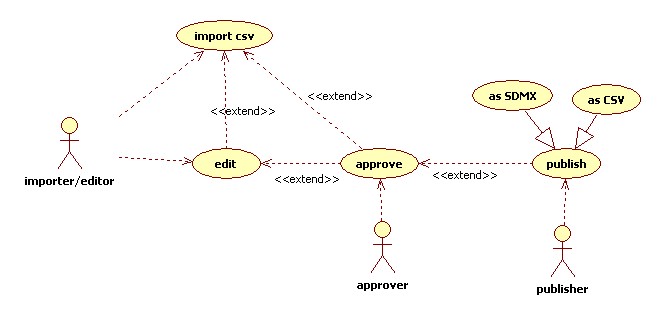
Core Use Cases
UseCase import csv
A good example for the import csv file is the ASFIS species list. The Asfis species list is a zip file, containing the file ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt, which is a csv file. The implicit hierarchies in this file are documented here. http://www.fao.org/fishery/collection/asfis/en documented here http://km.fao.org/FIGISwiki/index.php/ASFIS_SDMX_Codelist
After having imported the ASFIS file, the following codelists are interpreted:
- ASFIS Species Alpha 3 Codelist
- ASFIS Species Taxonomic Codelist
- ASFIS Species Family Taxonomic codelist
- ASFIS Species Order Taxonomic codelist
and hierarchies:
- Relation ASFIS Species Taxonomic code - Alpha 3 code
- Relation ASFIS Family - Species
- Relation ASFIS Order - Family
and collections
- ASFIS List of Species
Interpreted means that the system is capable of understanding all the implicit relations in the tabular format file like the the ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt file and shows in the UI distinguished codelists, hierarchies and collections. The ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt file results therefore in 4 codelits, 3 hierarchies and 1 collection.
The collection ASFIS List of Species is containing the same information as the original ASFIS_sp_Feb_2011.txt file.
UseCase create new version of an Artefact
- Start from scratch, import, or copy an existing Artefact in order to work on a new version of an Artefact.
- Delete codes/hierarchies
- Add codes/hierarchies
- Edit codes/hierarchies
- View deleted codes/hierarchies
- View added codes/hierarchies
- View edited codes/hierarchies
- Make Artefact final
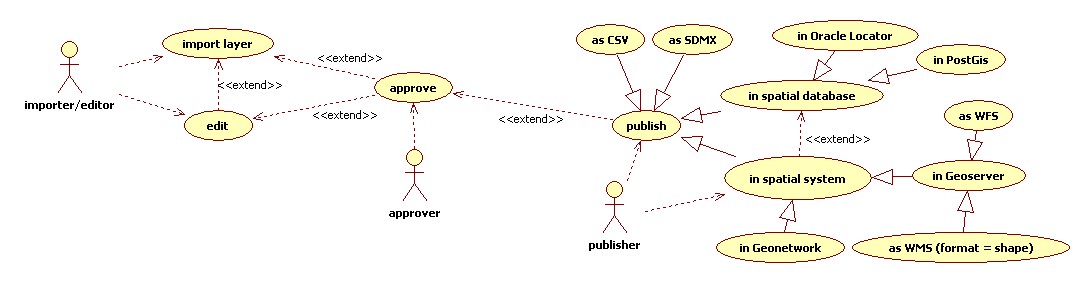
UseCase approve
A collection, codelist, hierarchy is approved and is ready to be published.
UseCase publish
A Collection, Codelist or Hierarchy can be published through SDMX, CSV:
- Codelists are published as SDMX codelists according the SDMX REST specifications.
- Hierarchies are published as SDMX hierarchical codelists according the SDMX REST specifications
- Collections are published as zip, txt, zip containing a txt file or zip containing a csv file. Such a collection would represent for instance the original ASFIS txt file.
UseCase publish geospatial referenced codelist
When codes have a geospatial reference through the attribute wellKnownText, it can be exported/published as a layer/WFSWeb Feature Service. Details of this usecase need to be refined further.
UseCase DiffReport
- User select artefact(Codelist, HierarchicalCodelist or Collection).
- User selects a certain version from that artefact.
- User selects another version from that same artefact.
- User clicks on generate DiffReport and views the DiffReport
The report shows:
- Codes added.
- Codes deleted.
- Number of codes in the first and second selected version.
UseCase Import Layer
- Import layer (shapefile)
- .... process generic edit and approve functions
- Publish as WFSWeb Feature Service, CSV, SDMX, WMSSee Workload Management System or Web Mapping Service.(format shape)
- Publish in PostGis
- Publish in Oracle Locator
The practical case behind this usecase is the FAO major areas:
http://km.fao.org/FIGISwiki/index.php/FMA_SDMX_Codelist
After having imported the FAO areas layer, the following codelists are interpreted:
- FAO Production Area codelist (from major area to sub-unit)
- FAO Major Water Area codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Subarea codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Division codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Subdivision codelist
- FAO Major Water Area Subunit codelist
and hierarchies:
- Relation Area code - Subarea code
- Relation Subarea code - Division code
- Relation Division code - Subdivision code
- Relation Subdivision code - Subunit code
Rules
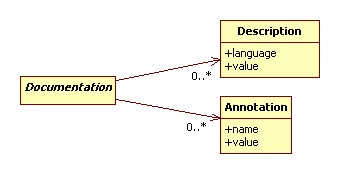
- The geometry is expressed as Well-known text(WKT) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Well-known_text
- Language dependent attributes from the shapefile are expressed as descriptions
- Non language dependent attributes from the shapefile are expressed as annotations
Core Rules
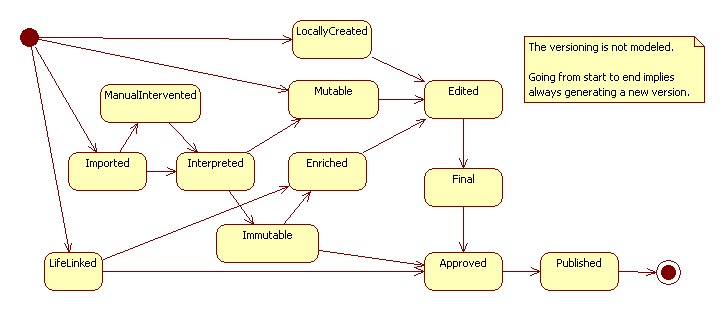
- A code can become final when:
- it is published in a codelist
- it is made final
- A code becomes non final when it was final and has been changed
- A code is non final when it is created
- A code can only change from final to non-final when it was not yet published in a codelist
- Changing the validityPeriod, wellKnownText or value of a final code will result in a copy of that code. The new code will be non final.
- Creating a new Code means also creating a new CodeLife
- Making a copy of a Code results in adding a link from that new Code to its CodeLife
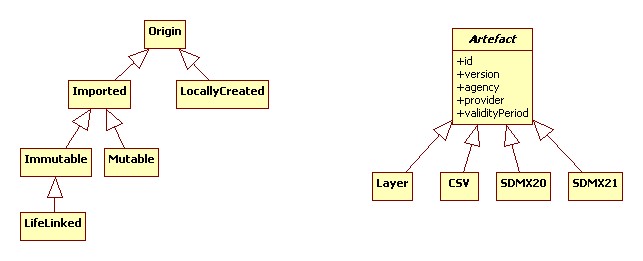
- An Artefact or Code has a type:
| Type (Artefact or Code) | Description |
| Local | This is the default type. Created or imported and the further lifecycle and management is in the system |
| ImportedImmutable | Imported from outside and cannot be changed. Will have a CodeLife. The lifecycle and management is outside of the system but will be followed and monitored in the system. |
| LifeLinked | Is only linked, not stored and at most cached. Works in principle only in case the outside link is available. Will not have a CodeLife, the lifecycle and management is outside of the system |
Nice to haves
- Integration with SharePoint
- Support for CMIS
- Export to OWL
- Export to SKOSS
- Export to RDF
- Merging
- Mapping
Links
[1]TaxoTools